Russia Denies that North Korea Is Supplying It With Weapons for Use in Ukraine
By Lionel Beehner
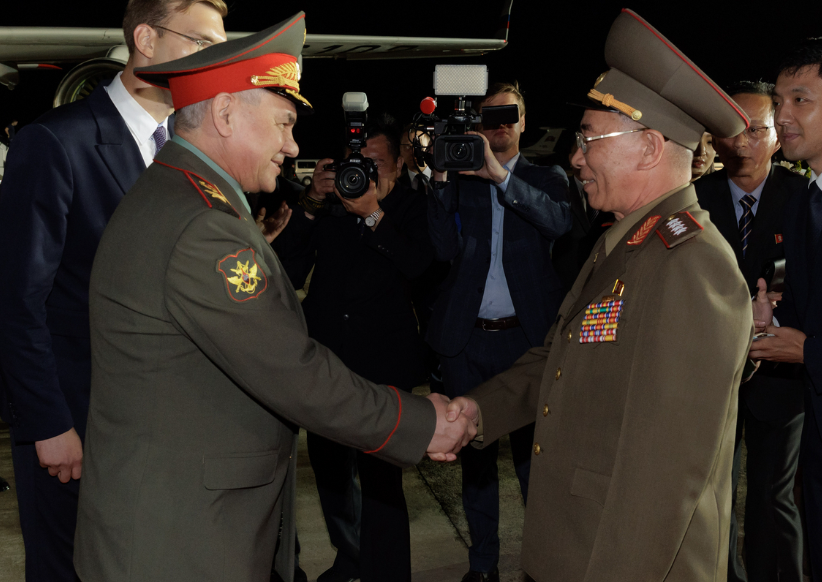

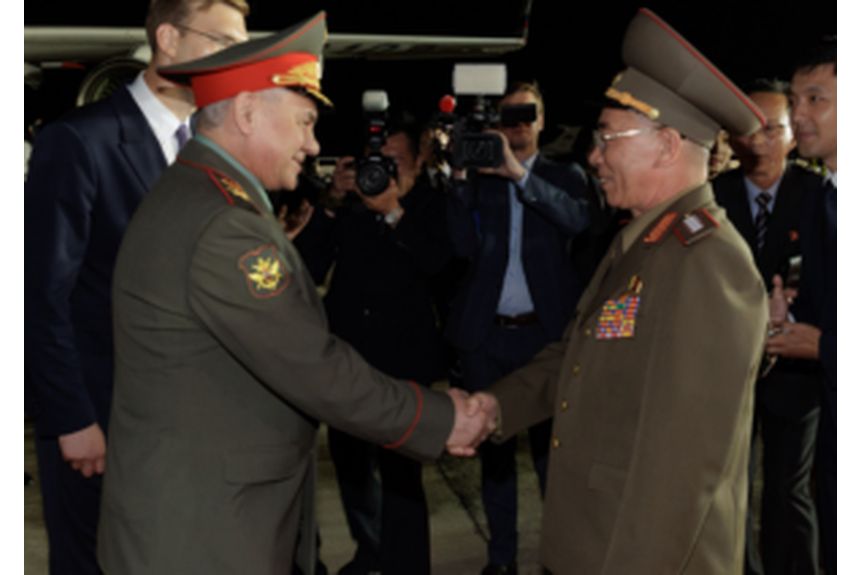
Meeting of Russian and North Korean Defense Ministers at Sunan International Airport in Pyongyang on 25 July 2023.
“The accusations made by the ‘collective West’ of ‘illegal’ military-technical cooperation between Russia and North Korea are unfounded and unsubstantiated.”
Relations between Russia and North Korea are drawing concern as new evidence emerges that Pyongyang has supplied Moscow with conventional munitions and missiles for use in Ukraine. Satellite activity from October 2022 revealed that North Korea supplied an arsenal of weapons – including short-range ballistic missiles, anti-tank missiles, and portable anti-air missiles as well as rifles, rocket launchers, mortars and shells.[i] If confirmed, North Korean sales of weapons to Russia would violate several UN Security Council resolutions (1718, 2270, and 2321) going back to 2006, which ban the sales of all arms, ballistics systems, and related materials to and from Pyongyang.
It is estimated Russia received some 350,000 artillery shells from North Korea. At a rate of fire of 10,000 per day at its high at the time of this writing (down from an estimated peak of 60,000 per day in 2022[ii]), that gives Russia just short of a two months’ supply. To put that figure in comparison, given American production levels of 24,000 artillery shells per month, that is more than the US produces in an entire year. The slower pace of Russian missiles fired (based on the 10,0000 per shells per day statistic) on Ukrainian cities could reflect its lack of supply, or it could be a sign of stockpiling in anticipation of a winter offensive, as some analysts suspect.[iii]
For its part, Russia’s foreign ministry has vehemently denied any violations. According to the excerpted article in the pro-Kremlin news site Sputnik News, Russia denies any “illegal” weapons transfers. Yet satellite imagery starting in August 2023 captures some 1,000 containers leaving North Korea’s Rajin port bound for an ammunition dump near Ukraine’s border.[iv] Indeed, as of October 2023, research from CSIS indicates that cross-border activity at North Korea’s Tumangang Rail Facility has spiked to its highest levels since before the pandemic.
In exchange, Russia has reportedly provided technical support to North Korea’s nascent space program, as well as ICBM technology. Such assistance is likely needed given Pyongyang’s two previous attempts to launch reconnaissance satellites failed due to booster malfunctions. Theodore Postol of MIT has suggested that Russia also supplied North Korea with the Topol-M [R1] ICBM, the basis for its solid-fuel Hwasong-18 [RG2] missile.[v] Though these reported arms transfers are notable, the Russia-North Korean nexus is not new. After the Cold War, observers raised fears that out-of-work Russian nuclear scientists were assisting Pyongyang to develop nuclear weapons. Today, fears of an arms race are rising in Seoul.[vi] That has prompted South Korea, Japan, and the U.S. to begin sharing real-time missile warning data emanating from North Korea.[vii] Experts disagree whether the Russia-North Korea nexus is a sign of Russian weakness (Russia is badly in need of arms) or strength (Moscow has allies and an arsenal it can call on rapidly for arms). Whatever the assessment, this nexus bears attention from the U.S. Army.
Sources:
“МИД РФ отрицает нарушение резолюций СБ ООН по Северной Корее (Russian Foreign Ministry Denies Violating UNSC Resolutions on North Korea),” Sputnik News (pro-Kremlin news outlet directed at foreigners), 11 November 2023. https://sputnikglobe.com/20231111/russian-foreign-ministry-denies-violating-unsc-resolutions-on-north-korea-1114884101.html
“The accusations made by the ‘collective West’ of ‘illegal’ military-technical cooperation between Russia and North Korea are unfounded and unsubstantiated … Russia is responsible in fulfilling its international obligations, including Security Council resolutions. This does not prevent us from deepening traditional relations of friendship and cooperation with our neighbors, including North Korea,” Russian Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova was quoted as saying by the Russian Foreign Ministry.
Russian Foreign Ministry Ambassador at Large Oleg Burmistrov told Sputnik that Russia thoroughly abides by its international obligations towards Pyongyang within the Security Council’s resolutions.
Earlier in the day North Korean Foreign Ministry said in a statement distributed by the Korean media that friendship between Russia and North Korea will only strengthen in the future, and the United States will face a “powerful and coordinated response” if it attempts to disrupt stability in the region.“Relations of friendship and cooperation between two countries – Korea and Russia, striving for independence, peace and friendship, will unshakably strengthen and develop, and any attempts by the United States and its satellites aimed at disrupting peace and stability on the Korean Peninsula and in the region will face a powerful and coordinated response from independent sovereign states,” the statement said. It said the US administration should get used to the “new realities of Korean-Russian relations.”
Notes:
[i] Joseph S. Bermudez Jr., Victor Cha and Jennifer Jun, “Ongoing Arms Transfer Activity at Najin Port,” Beyond Parellel, CSIS, 17 October 2023. https://beyondparallel.csis.org/ongoing-arms-transfer-activity-at-najin-port/
[ii] Jeff Schogol, “Russia is hammering Ukraine with up to 60,000 artillery shells and rockets every day,” Taks and Purpose. 13 June 2022. https://taskandpurpose.com/news/russia-artillery-rocket-strikes-east-ukraine/
[iii] Dara Massicot, “Putin’s Cannon Fodder: Foreign Affairs Interview,” Foreign Affairs, 2 November 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D2sUEB_rRhA
[iv] The shipment came shortly before the leaders of Russia and North Korea met for five hours at Russia’s Vostochny Spaceport, according to TASS, the Russian News Agency. See: Five hours at Vostochny Spaceport: Putin, Kim Jong Un meet again four years later,” TASS (Russia’s main state news agency), 13 September 2023. https://tass.com/politics/1674459: The satellite imagery is further backed up by recent analysis by the Royal United Services Institute (RUSI) that found that two Russian vessels made at least five round trips between North Korea and Russia, believed to be arms transfers. See: Song Sang-Ho, “2 Russian ships made 5 trips between N. Korea, Russia since mid-Aug. in suspected arms transfers,” YonHap News Agency (South Korea’s leading news agency) 17 October 2023. https://en.yna.co.kr/view/AEN20231017000351315
[v] Theodore Postol of MIT suggests that Russia also had supplied North Korea with the Topol-M ICBM, the basis for its solid-fuel Hwasong-18 missile. See: Theodore Postol, “The Transfer of a Russian ICBM to North Korea?” Beyond Parallel, 17 August 2023. https://beyondparallel.csis.org/the-transfer-of-a-russian-icbm-to-north-korea/
[vi] Simon Hutagalung, “Russia and North Korea relations in transition,” Korea Times (English-language newspaper in Seoul), 5 November, 2023. https://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/opinion/2023/11/137_362456.html
[vii] Anastasia Kostina, “Учения обстоятельств: США и Южная Корея отработают оборону от КНДР (Exercises of circumstances: the United States and South Korea will practice defense against the DPRK: How Pyongyang and Beijing react to the maneuvers of Washington and Seoul),” Izvestia (Russian news outlet), 30 October 2023. https://iz.ru/1596255/anastasiia-kostina/ucheniia-obstoiatelstv-ssha-i-iuzhnaia-koreia-otrabotaiut-oboronu-ot-kndr
Image Information:
Image: Meeting of Russian and North Korean Defense Ministers at Sunan International Airport in Pyongyang on 25 July 2023.
Source: Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Meeting_of_Russian_and_North_Korean_Defense_Ministers_(2023)_01.png
Attribution: CCA 4.0
Distribution A: Approved for public release
Categories:
Tags:
Related Products
Chinese Military Exercises Highlight Improvements in Joint Operations
North Korean Media Stays Quiet Despite Global Concerns