Russia Signs Agreement To Open Naval Base In Abkhazia
By Dodge Billingsley
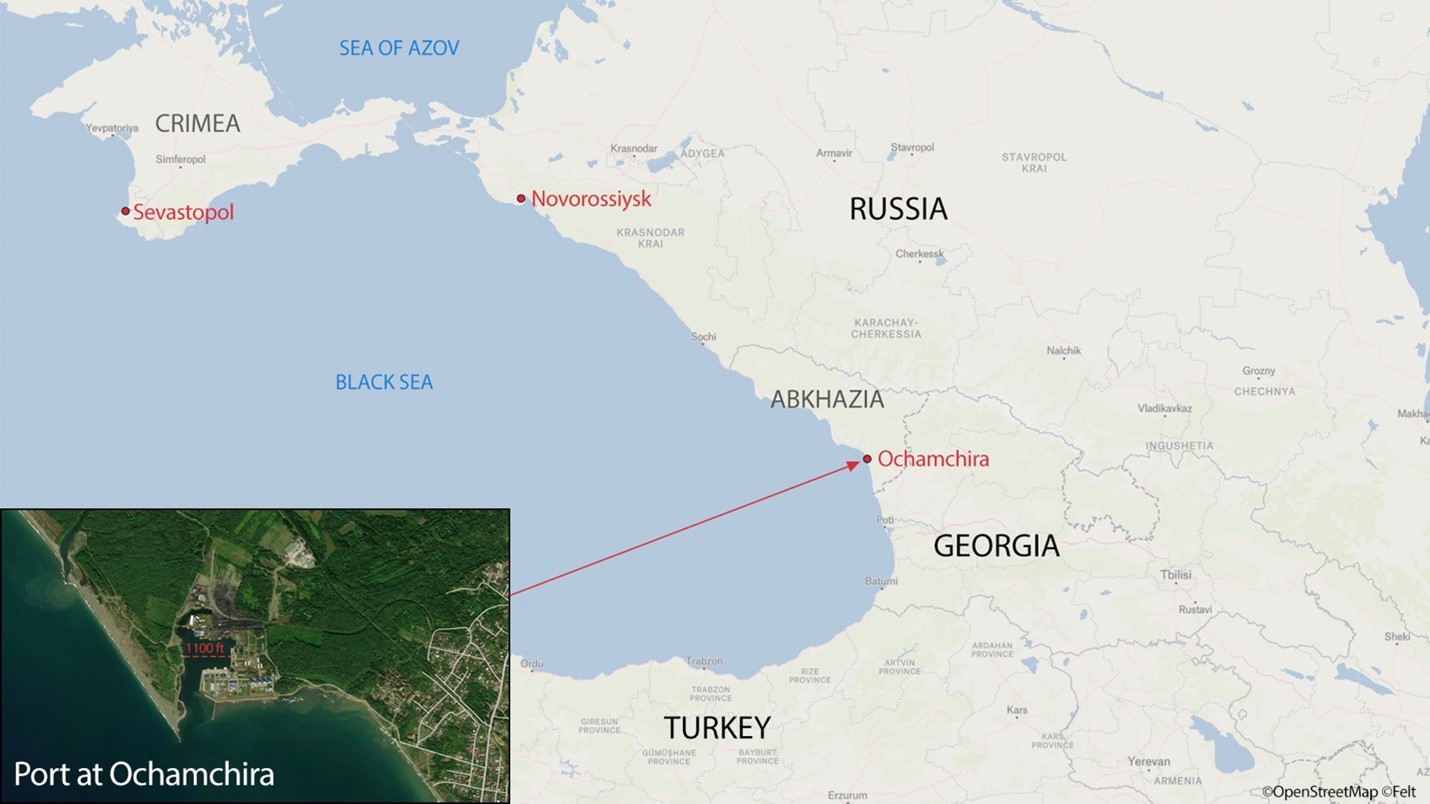
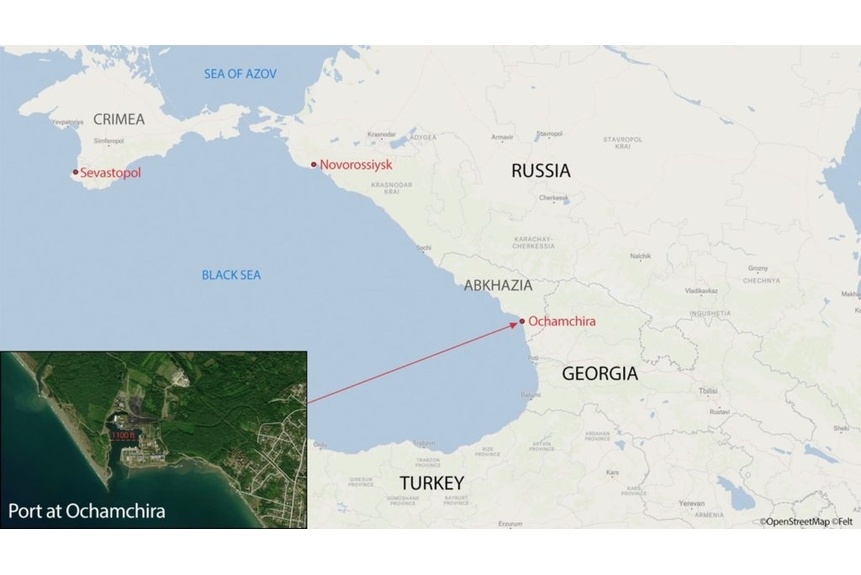
Map of Russian Black Sea naval bases Sevastopol and Novorossiysk and the proposed base at Ochamchira on disputed Georgian territory.
“The interaction between Moscow and Sukhum in terms of military-technical cooperation is aimed at increasing the level of defense capability of both Russia and Abkhazia, says Bzhania.”
Abkhazia has signed a bilateral agreement to host a Russian naval base near the southern Abkhazian city of Ochamchira. Western observers have interpreted the announcement as proof Ukraine is having success driving Russia’s Black Sea Fleet out of Crimea, while the Russian and Abkhazian press are focused on the regional implications of the proposed Russian naval base.
According to the first excerpted article from the Russian daily Izvestia,[i] the agreement is intended to increase defense cooperation between Russia and Abkhazia, recognized as an independent state by Russia.[ii] However, the second excerpted article from the regionally focused Echo Kavkav points out, Russian coastal patrol boats already use the port at Ochamchira. This port is small in comparison to Novorossiysk, the naval port to which Russia has moved much of its Black Sea fleet after Ukraine demonstrated it is capable of attacking naval assets at Sevastopol on Crimea. According to political figure and Hero of Abkhazia[iii], Aslan Kobakhia, the announcement is part of the information war between pro-Russian Abkhazians and those Abkhazians who prefer a more independent political path for Abkhazia. He noted there has been talk of an expanded base in Ochamchira for years, further observing that “no matter how deep you go, it’s a small port, only a few ships can be there at a time, and large ships cannot base there.” However, Kobakhia did conclude an expanded port at Ochamchira could be used as a vital refueling hub for Russia’s Navy. According to Giva Kvarchia, as quoted in the third excerpted article from the Abkhaz diaspora media website Abkhaz World, the base in Abkhazia would be mutually beneficial as it would be an economic boon to Abkhazia and provide a military advantage to Russia. A base at Ochamchira would also serve as a deterrent against any future military action by Georgia to take back Abkhazia. Kvarchia acknowledged that the base would be provocative and both “a protection and a potential threat.” A Russian naval base in Abkhazia presents an interesting security dilemma for the region. Ukraine has proven capable of attacking Russian naval vessels in Novorossiysk, Russia, and Sevastopol, on the Ukrainian Crimean Peninsula, which has been annexed by Russia. Given that Abkhazia is not Russian territory, any decision to engage the Russian Navy there would necessarily be seen as an attack on the territory.[iv] While, the announcement of the Russian naval base in Abkhazia is merely that, the positioning of additional Russian assets there could impact the operational environment of the whole eastern Black Sea region.
Sources:
“Бжания сообщил о размещении в Абхазии пункта постоянного базирования ВМФ РФ (Bzhania announced the deployment of a permanent base for the Russian Navy in Abkhazia), Izvestia (pro-Kremlin daily newspaper), 05 October 2023. https://iz.ru/1584377/2023-10-05/bzhaniia-soobshchil-o-razmeshchenii-v-abkhazii-punkta-postoiannogo-bazirovaniia-vmf-rf
A new permanent base for the Russian Navy will appear on the Black Sea coast in Abkhazia; a corresponding agreement between Russia and Abkhazia has already been signed, Abkhaz President Aslan Bzhania said in an interview with Izvestia.
“Two states, but we have a common Fatherland”
“On the day of our holiday [in honor of the 30th anniversary of Victory Day in the Georgian-Abkhaz war of 1992–1993 and Independence Day, which was celebrated on September 30], a small missile ship came to us, we boarded it – a very modern ship with serious combat capabilities . We have signed an agreement, and in the near future there will be a permanent base for the Russian Navy in the Ochamchira region,” Bzhania said.
In addition, the President of the Republic noted that Russia continues to provide support, providing the opportunity for Abkhaz specialists to undergo advanced training in educational institutions of the Russian Federation.
The interaction between Moscow and Sukhum in terms of military-technical cooperation is aimed at increasing the level of defense capability of both Russia and Abkhazia, says Bzhania.
From August 21 to September 1, 2023, joint Russian-Abkhaz military special-purpose, flight and tactical exercises were held in four regions of Abkhazia, aimed at increasing the level of field training of troops and forces, coordinating their actions when performing combat missions.
Russia recognized the sovereignty of Abkhazia on August 26, 2008. This year, ceremonial events were held in the republic in honor of the 15th anniversary of this event. Currently, the Russian and Abkhaz military jointly ensure the security of the republic. Also, the borders of Abkhazia are guarded by the border service of the Russian FSB.
Vitaly Shariya, “Аслан Кобахия: «Шум вокруг Очамчырского морпорта – буря в стакане воды» (Aslan Kobakhia: ‘The noise around the Ochamchira seaport is a storm in a teacup’),” Ekho Kavkaza (regionally specific news source), 12 October 2023. https://www.ekhokavkaza.com/a/32634876.html
“I’ve been there several times. No matter how deep you go…’It’s a small port. Only a few ships can be there at a time. There are no such opportunities that some people are talking abo–t – they left Sevastopol, they left Novorossiysk… The Russian fleet cannot leave either Sevastopol or Novorossiysk, there are no such opportunities. Five percent of those ships will not fit on the territory of Abkhazia. You need to know a little to speak. There is no place to base large ships there. Ships can enter there, refuel, and go back to sea. The Russian Federation doesn’t comment at all, but here we start, you know, creating a storm in a teacup… Why, I can’t understand.”
“Givi Kvarchia: ‘Military Bases: A Double-Edged Sword of Protection and Threat,’ Abkhaz World (pro-Abkhaz web news service run by Abkhaz diaspora in Europe), 6 October 2023. https://abkhazworld.com/aw/interview/2536-givi-kvarchia-military-bases-a-double-edged-sword-of-protection-and-threat?utm_source=substack&utm_medium=email
[Q]. Aslan Bzhania also made a statement indicating that Sukhum is prepared to deepen its military-technical cooperation with the Russian Federation, and that a new permanent base for the Russian Navy will be established on the Black Sea coast in Abkhazia. Could you comment on this matter?
[Givi Kvarchia]. As for the enhanced military-technical cooperation between our nations, it is already outlined in the broader alliance and strategic partnership agreement, as well as in interdepartmental agreements between our defence ministries. This ’sn’t a new development; it has been in planning for a long time. Perhaps it h’sn’t proceeded at the pace’we’d desire, especially in terms of military-technical cooperation. Regarding the Ochamchira port and the basing of certain Black Sea Fleet ships or a portion of it there, this ’sn’t new in Abkhazian politics either. Discussions and negotiations about the joint use of the Ochamchira port by the Russian Federation and the Republic of Abkhazia have been ongoing for years, and as far as I know, an agreement has been reached to use this port on mutually beneficial terms.
[Q]. Givi, could you elaborate on the essence of the“e “mutually beneficial te”ms”?
[Givi Kvarchia]. The crux of it is that a portion of this port will be used by the Abkhazian side for economic purposes. Meanwhile, another portion will tilizedsed by the Russian Federation for military objectives.
[Q]. Givi, considering the war in Ukraine and recent information that a drone made its way to Sochi, a’en’t you concerned that a Naval base in Ochamchira might pose a security threat to the citizens or the country as a whole? What are your thoughts?[Givi Kvarchia]. Any military base or basing point can serve as both protection and a potential threat. However, our discussions about the Ochamchira port began before the military operation in Ukraine unfolded. To put it simply,’it’s a double-edged sword, but from our perspective, it represents more of a security measure than a threat, in my view.
Notes:
[i] Although Russian media outlet Izvestia broke the story of the proposed Russian naval base at Ochamchira, there was very little additional Russian coverage of the topic. In a separate article from Izvestia, Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov deferred on the topic, noting that it was a military issue and inferring that questions about the basing agreement should be directed to the Russian Ministry of Defense, see: “Песков переадресовал вопрос о размещении ВМФ в Абхазии в Минобороны (Peskov forwarded the question about the deployment of the Navy in Abkhazia to the Ministry of Defense), Izvestia, 5 October 2023. https://iz.ru/1584547/2023-10-05/peskov-pereadresoval-vopros-o-razmeshchenii-vmf-v-abkhazii-v-minoborony
[ii] Abkhazia, and South Ossetia, are break-away republics within the Republic of Georgia. Georgia considers both territories occupied by Russia, which is not factually accurate, especially in the case of Abkhazia which has fought to be recognized as an independent state and maintains its own security apparatus. Only a handful of countries have recognized Abkhazia’s independence: Russia, Venezuela, Nicaragua, Nauru and Syria.
[iii] Hero of Abkhazia, much like Hero of the Russian Federation, is a title given to Abkhazians who have performed a heroic deed in the service of the state, usually veterans of the war between Abkhazia and Georgia (1992-1993).
[iv] For more on current Russia-Abkhazia relations see: Dodge Billingsley “Abkhazia Pushes Back Against Russia’s Suggestion Of Incorporation,” OE Watch, 08-2023. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2023/abkhazia-pushes-back-against-russias-suggestion-of-incorporation/
Image Information:
Image: Map of Russian Black Sea naval bases Sevastopol and Novorossiysk and the proposed base at Ochamchira on disputed Georgian territory.
Source: Combat Films and ResearchAttribution: Combat Films and Research by permission using map data from OpenStreetMap
Distribution A: Approved for public release
Categories:
Tags:
Related Products
Chinese Military Exercises Highlight Improvements in Joint Operations